You are Here: Process Software>> A Complete Guide for Business Process
Table of Contents
- What is a Business Process?
- Types of Business Processes
- What is Business Process Technology?
- The Importance of Business Processes
- Key Reasons to have well-defined Business Processes
- Business Process Example
- Business Process Life Cycle
- Benefits of using Business Process Software
- Essential Attributes of an Ideal Business process
- What are Some Terms Related to Business processes?
Everyone talks about business processes, but there remains a lot of confusion regarding them. To provide some clarity, here is all the information you’ll need regarding what they are, and why your business needs to understand them.
What is a Business Process?
A business process is defined as a series of tasks or a set of activities performed by a group of stakeholders to achieve an organizational goal. The processes are performed by people or systems in a structured manner to attain a pre-defined objective. Efficient and streamlined execution of business processes directly contributes to the success of business operations and growth.
A business process has also been defined in simple terms as a set of activities and tasks that, once completed, will accomplish an organizational goal.
Each step in a business process denotes a task that is assigned to a participant. It is the fundamental building block for several related ideas such as business process management, process automation, etc.
While there’s a deluge of things written and said about business process management, it’s essential to understand why they are so important to your business.
Types of Business Processes
1. Core Processes
These processes are the critical functions of a business that directly add value to the end customers. These processes are critically aligned with the fundamental values, objectives, and vision of the business. Businesses must continuously monitor and improve these processes as they primarily contribute to the growth and revenue flow of the organization.
2. Support Processes
These processes enable and support the core processes to be performed seamlessly. Although they do not contribute to revenue generation, they assist internal departments in creating a collaborative environment where the core processes can be aligned to work better. Human resources, finance management, administration, and operations fall under supporting processes as they help expand a business.
3. Management Processes
These processes are responsible for planning, monitoring, managing, and controlling the core and supporting processes from start to end. These processes are goal-oriented and ensure that business operations are carried out efficiently and seamlessly. Their focus is to monitor business functionalities internally and externally, analyze opportunities and challenges, and ensure continuous improvement of all processes.
Business Process Technology
Business process technology refers to the use of technology, such as software and systems, to automate, streamline, and optimize business processes. It helps organizations improve efficiency, reduce errors, and save time and resources on manual task completion. It can be customized as per needs and can be used in a variety of industries. Workflow management software, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are a few examples of business process technology.
The Importance of Business Processes
The need for and advantages of a business process are quite apparent in large organizations. A process forms the lifeline for any business and helps it streamline individual activities, making sure that resources are put to optimal use.
Key reasons to have well-defined Business Processes
- Identify what tasks are important to your larger business goals
- Improve process efficiency
- Streamline communication between people/functions/departments
- Set approvals to ensure accountability and optimum use of resources
- Prevent chaos from creeping into your day-to-day operations
- Standardize a set of procedures to complete tasks that really matter to your business
An Example of a Business Process
As an example, let’s consider the hiring process of an HR department. Right from posting the job opening to onboarding the employee, there are multiple steps involved in the process. Although this can vary from organization to organization, a simple workflow might look like this:
- The HR executive posts the job update
- Multiple candidates apply in a portal
- The HR executive screens the candidates and filters the best-fits
- The selected candidates are called for the next stages of the recruitment
- The right candidate is chosen at the last stage of the recruitment
- Salary and policy negotiations take place
- The offer letter is sent and the candidate accepts
This is then followed by a long employee onboarding process.
☛ Here are 6 real-world business process examples.
An incredibly easy way to automate business processes
The 7 Steps of the Business Process Lifecycle
Here are the seven steps in the business process lifecycle.
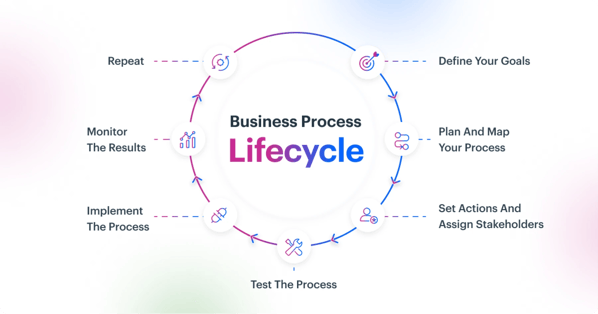
Step 1: Define Your Goals
What is the purpose of the process? Why was it created? How will you know if it is successful?
Step 2: Plan and Map Your Process
What are the strategies needed to achieve the goals? This is the broad roadmap for the process.
Step 3: Set Actions and Assign Stakeholders
Identify the individual tasks your teams and machines need to do in order to execute the plan.
Step 4: Test the Process
Run the process on a small scale to see how it performs. Observe any gaps and make adjustments.
Step 5: Implement the Process
Start running the process in a live environment. Properly communicate and train all stakeholders.
Step 6: Monitor the Results
Review the process and analyze its patterns. Document the process history.
Step 7: Repeat
If the process is able to achieve the goals set for it, replicate it for future processes.
Streamline and standardize your business processes
Benefits of using Business Process Software
BPM solutions are uniquely designed to boost the efficiency of processes across verticals and organizations. Implementing them brings a host of business benefits such as:
1. Reduction of Risks
BPM software helps prevent and fix errors and bottlenecks thereby minimizing risks.
2. Elimination of Redundancies
Monitoring processes allows for identification and elimination of duplicated tasks. Implementing BPM software also enhances resource allocation to ensure human effort is invested only in relevant tasks.
3. Minimized Costs
Improved visibility into processes helps zero in on wasteful expenditure. This way costs are kept to a minimum and savings are boosted.
4. Improved Collaboration
Transparency fostered by BPM software boosts collaboration between internal teams as well as external vendors and buyers. Everyone is aware of responsibilities as well as timelines and bottlenecks.
5. Agility
Optimized processes enable greater agility in organizational operations. Minimized errors, bottlenecks, and duplication facilitate quicker turnaround times.
6. Improved Productivity
When processes are shipshape, approvals are faster and information retrieval is easier. Tasks are routed sequentially without human intervention. These benefits significantly boost productivity of teams.
7. Higher Efficiency
Comprehensive dashboards in BPM software provide bird’s-eye view of process performance. It helps managers ensure that turnaround times are short and accuracy levels are high.
8. Higher compliance
With BPM software, it’s easier and more methodical to create audit trails and comply with industry regulations and standards.
What are the Essential Attributes of an Ideal Business Process?
There are 4 essential attributes that constitute an ideal business process:
1. Finite
A good business process has a well-defined starting point and ending point. It also has a finite number of steps.
2. Repeatable
A good business process can be run an indefinite number of times.
3. Creates value
It ultimately aims at translating the creation of value into executable tasks and does not have any step in the process just for the sake of it. In other words, if any step in the process isn’t adding value, it should not exist.
4. Flexibility
It has an in-built nature to be flexible to change and is not rigid. When there is any scope for improvement that is identified, the process allows that change to be absorbed within itself without operationally affecting its stakeholders as much.
☛ Case Study Alert:
Check out How Kissflow helped Softbank Telecom by creating 25+ Apps
What are some of the terms related to Business Processes?
1. Business Process Automation
Business process automation is a technology-driven strategy to automate a business process in order to accomplish it with minimum cost and in a shorter time. It is extremely useful for both simple and complex business processes. Some of the benefits of business process automation are:
- Achieving greater efficiency
- Reducing human error
- Adapting to changing business needs
- Clarifying job roles and responsibilities
2. Business Process Management
BPM is a systematic approach to make an organization’s processes more efficient and dynamic in order to meet the changing needs of business. Continuous improvement is one of the core underlying philosophies of BPM and it aims to put it at the centre of all BPM initiatives. BPM is an ongoing approach to continuously make execution of business processes better. Several cloud and on-premise software solutions are available to implement BPM.
3. Business Process Modeling
Business process modeling is a diagrammatic/structural representation of flow of business activities in an organization or function within an organization. Its primary use is to document and baseline the current flow of activities in order to identify improvements and enhancements for speedy accomplishment of tasks. Usually, they follow a standard such as Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN), which is a globally accepted standard that most process professionals easily identify with. However, process modeling software like Kissflow enables even a business user to model a process based on business steps, without having to know any modeling notation.
4. Business Process Improvement
Business process improvement is a strategic planning initiative that aims at reshaping business processes based on operations, complexity levels, employee skills, etc. in order to make the entire process more meaningful, efficient, and contribute to overall business growth. It is a rather drastic way to rediscover more efficient ways to run a business process rather than taking small incremental steps. It usually starts with process mapping and its core aim is to align IT resources with organizational business goals. There are a lot of process improvement tools in the market that’ll help you out with this.
5. Business Process Development
Business Process Development and Management(BPDM) is the holistic process of designing, creating, and implementing new business processes or modifying existing ones. BPDM involves identifying the steps and activities required to achieve a specific business goal, and designing a process that is efficient, effective, and aligned with the organization's overall strategy.
6. Business Process Reengineering
Business process reengineering is a complete redesign of business processes after thorough analysis in order to bring drastic impact. It involves identifying the core of inefficiency, culling out tasks that don’t add any value, and even implementing a top-to-bottom change in the way a process is designed in order to bring about an overall transformation.
7. Business Process Optimization
Business process optimization takes an existing process and uses analytics and business process mining tools to weed out bottlenecks and other significant inefficiencies in a process.
8. Business Process Mapping
Business process mapping is a procedure to document, clarify, and break down process sequences into logical steps. The mapping is either done in written format or visualized using flow charts. Choose a process mapping software that empowers business users to map all the processes based on logical steps with an intuitive visual interface.
9. Business Process Analysis
Business process analysis is the process of identifying business requirements and deciding on solutions that best solve business problems. This can consist of process improvement, policy development, organizational change, or strategic planning.
10. Business Process Integration
Business process integration is the ability to define a process model that defines the sequence, hierarchy, events, and execution logic and movement of information between systems residing in the same enterprise.
11. Business Process Simulation
Business process simulation is a tool for the analysis of business processes to measure performance, test process design, identify bottlenecks, test changes, and find how a process operates in different environmental conditions with different datasets.
12. Business Process Transformation
Business process transformation is a term that means radically changing a series of actions needed to meet a specific business goal. This is aimed at ensuring that a company’s employees, goals, processes, and technologies align with each other.
13. Business Process Flow
The Business process flow is a representation of the process that you’re creating. It usually looks like a form or flow chart. Every business process flow is composed of stages, and inside each stage, there are fields (or steps) to complete.
14. Business Process Monitoring
Business process monitoring is the active monitoring of processes and activity to help management gain insight into important transactions and processes within an enterprise. This helps management understand how their processes are functioning, and if they’re aligned with the company’s business goals.
Time to create your Business Processes
Well-designed business processes set up your teams on the path to success. Everyone is clear on their roles and responsibilities and work with a clear vision towards the end goal.
The situations when companies hired expensive consultants for designing business processes are fading away. You don’t want another person to create a business process for you when you are the expert that knows the in and out of your business.
Did you know you can create a business process in 15 minutes with Kissflow Process? The no-code platform keeps it simple while letting you design sophisticated business processes. Try it out and see how easy it is.
You may also like:
- What is BPM?
- What is BPMS? How Can It Help Your Organization?
- Best Business Process Management Software
- Business Process Strategy to Automate end to End Business Process
- The Keys to Achieve Operational Excellence Through Process Optimization
- BPM Systems – The Best one MUST (will) have these 10 features
- How To Make Simple & Effective Business Process.
- Business Process Hierarchy: The Ultimate Guide
